Chatbots once ignited a revolution in automation. AI made them smarter and more effective. Now, AI agents take a step forward, executing complex tasks without human intervention.
But are AI agents really the right fit for every business, and what makes them fundamentally different from the AI chatbots we’ve known so far?
Let’s talk about the key differences between AI agents and AI chatbots, their use cases, and implementation specifics to determine which solution works best for your business.
What is an AI Chatbot and How It Works
An AI chatbot is a software system designed to interact with users through text or voice. While conventional rule-based chatbots let the user engage only through menu items, AI chatbots use NLP and machine learning to understand user input and generate natural, contextual responses. This allows them to handle more complex tasks such as answering open-ended questions.
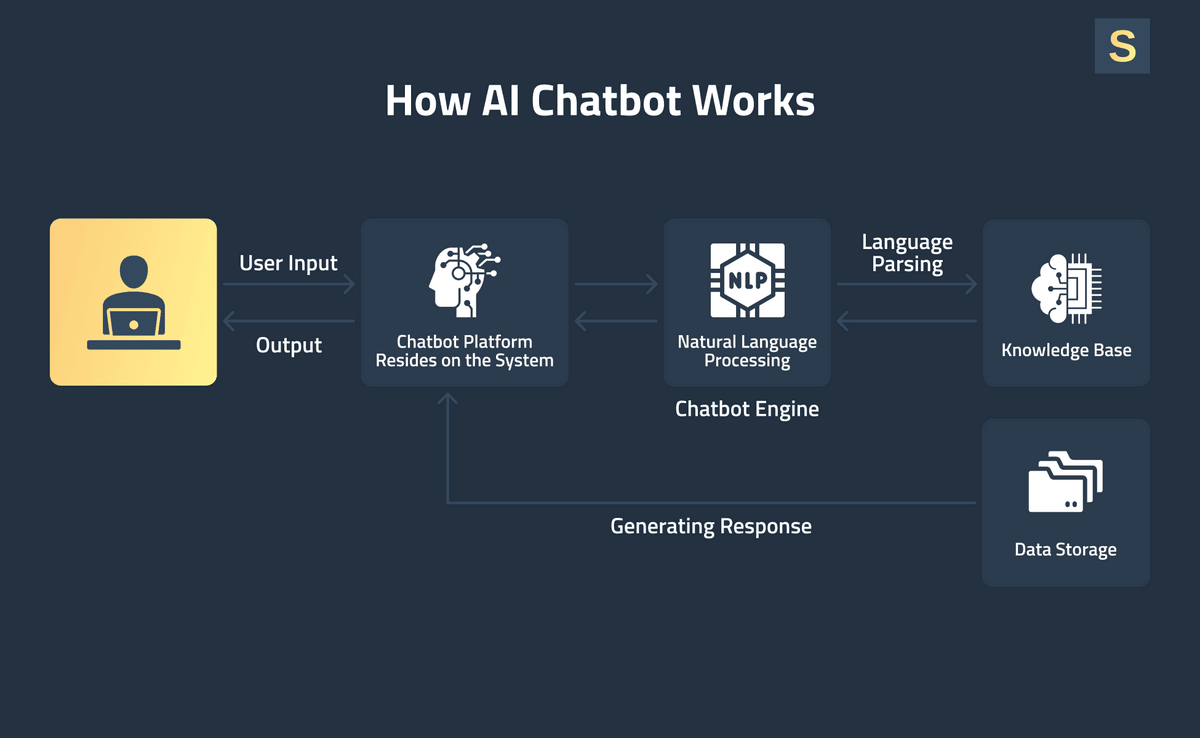
Under the hood, AI chatbots work like this:
- The bot receives the user’s input through a chat interface, such as a web page, mobile app, or messaging platform.
- The system preprocesses the text: removes punctuation, converts it to lowercase, and normalizes spacing.
- The bot maps the user input to a predefined intent using pattern matching, keywords, or a lightweight ML model.
- The system extracts structured data (entities) needed to perform the task, such as names, dates, IDs, or locations.
- The bot’s rules engine or flow chart determines the next action based on the detected intent and extracted entities.
- If required, it calls backend systems or APIs to fetch or update information.
- The bot selects the appropriate response template for the intent and fills in dynamic data as needed.
- Finally, it sends the message back to the user through the chat interface.
Even though this looks more advanced than traditional bots, AI chatbots’ capabilities are still limited compared to AI agents. The key drawback is that they can’t understand context beyond their training or act autonomously.
AI Chatbot Use Cases in Business
AI chatbots work well for simple, predictable flows that address specific business needs. Moreover, companies have greater control over conversations limited to a defined database. This ensures the responses stay within approved scenarios and maintain the brand voice.
Top 5 AI chatbot use cases include the following:
- Customer Support: AI chatbots can answer frequently asked questions, reducing the burden on human resources. They match customer queries to predefined responses and keep users engaged.
- Bookings & Appointments: A restaurant or hotel chain can implement an AI chatbot to manage bookings. When connected to the reservation system, it can check and suggest available times, handle cancellations, or reschedule.
- Financial Assistance: AI chatbots can analyze user spending habits and provide personalized saving advice when integrated with a user’s financial accounts, transaction history, or budgeting apps. They apply machine learning algorithms to detect spending patterns and generate recommendations.
- Onboarding: AI chatbots are great at helping employees navigate an organization’s knowledge base. This makes them an ideal tool for guiding newcomers through policies, procedures, and training materials.
- E-commerce Support: AI chatbots can deliver personalized product recommendations, helping users compare options, understand key differences, and even find the right size.
Read also: AI in SaaS: Use Cases and Best Practices
What is an AI Agent and How It Works
AI agents are autonomous and proactive systems. They are capable of completing multi-step tasks and making decisions. Unlike AI chatbots, AI agents are built on top of large language models (LLMs). This means they are trained on vast amounts of external data, not only on business datasets. They can provide deeply context-aware interactions and assist with complex tasks such as writing, coding, analysis, and creative problem-solving.
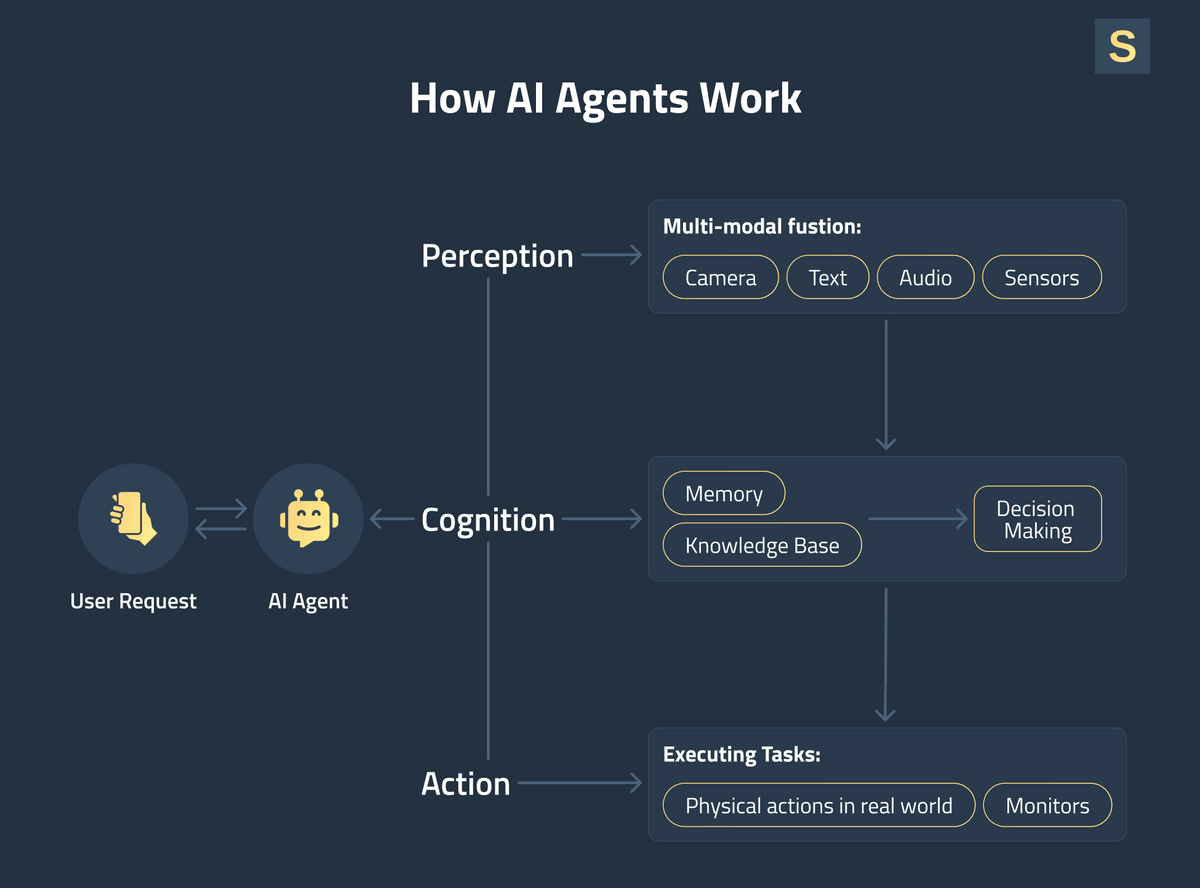
From a technical perspective, AI agents are far more complex than chatbots. They integrate with APIs for interacting with external systems, use memory to maintain context and personalize interactions, and employ reasoning to execute multi-step tasks autonomously.
This works as follows:
- The AI agent receives the user’s input through a chat interface, API call, voice assistant, or another trigger.
- The system preprocesses the input: cleans text, normalizes formats, and converts it into a structured representation.
- The agent uses an LLM to understand the user’s intent, extract relevant entities, and interpret context not only from the current session but also from past interactions.
- The agent breaks complex requests into actionable steps to determine the tasks needed to fulfill the request.
- If required, the agent autonomously selects and calls external tools or APIs to retrieve or update information.
- The agent generates context-aware, natural language responses and optionally suggests follow-up actions or asks clarifying questions.
- The agent updates its memory or logs to retain session context, user preferences, and task history for future interactions.
As you can see, AI agents are more advanced solutions that use stored context to provide more personalized and reliable responses over time.
AI Agent Use Cases in Business
Since AI agents are trained on larger datasets and deliver a fully natural conversational experience, they can handle more complex, multi-step tasks.
Top 5 AI agent use cases include the following:
- Productivity Management: AI agents can manage calendars, schedule meetings, draft and summarize emails, generate meeting notes, and streamline daily workflows.
- Hiring Automation: HR teams can use AI agents to screen candidates, schedule interviews, and refine hiring strategies using insights from past recruitment data.
- Marketing Support: AI agents can qualify leads, engage prospects, and follow up automatically, helping marketing teams scale outreach and improve conversion rates.
- Coding: AI agents excel as coding assistants. They can suggest best practices, refactoring options, and optimizations. At Seedium, we use these tools to streamline software development and modernization for our clients.
- Research: AI agents can collect, analyze, and summarize data from multiple sources, assisting with data visualization, reporting, and actionable insights.
Read also: Modernizing Legacy Systems With an AI-Assisted Approach
Limitations of AI Agents
Although AI agents offer significant potential, their autonomy can cause errors and unexpected failures. And because they are deeply rooted in workflows, an innocent mistake can bring down entire systems. Here are some examples:
- Incorrect API call: The agent sends a request with wrong parameters or in the wrong format, which causes issues in the workflow. For example, the agent tries to create a CRM record but sends invalid data.
- Reasoning error: The AI agent makes a wrong decision based on its logic. For example, the agent merges two leads with similar names, losing important information.
- Incorrect SQL: The agent generates a query that modifies or deletes data unintentionally.
- Wrong autonomous action: The agent performs an automated action that impacts operations or clients. For example, it may send incorrect emails, launch the wrong campaign, or trigger unintended transactions.
When developing AI agents, you should be aware of these risks and have mitigation and recovery plans in place.
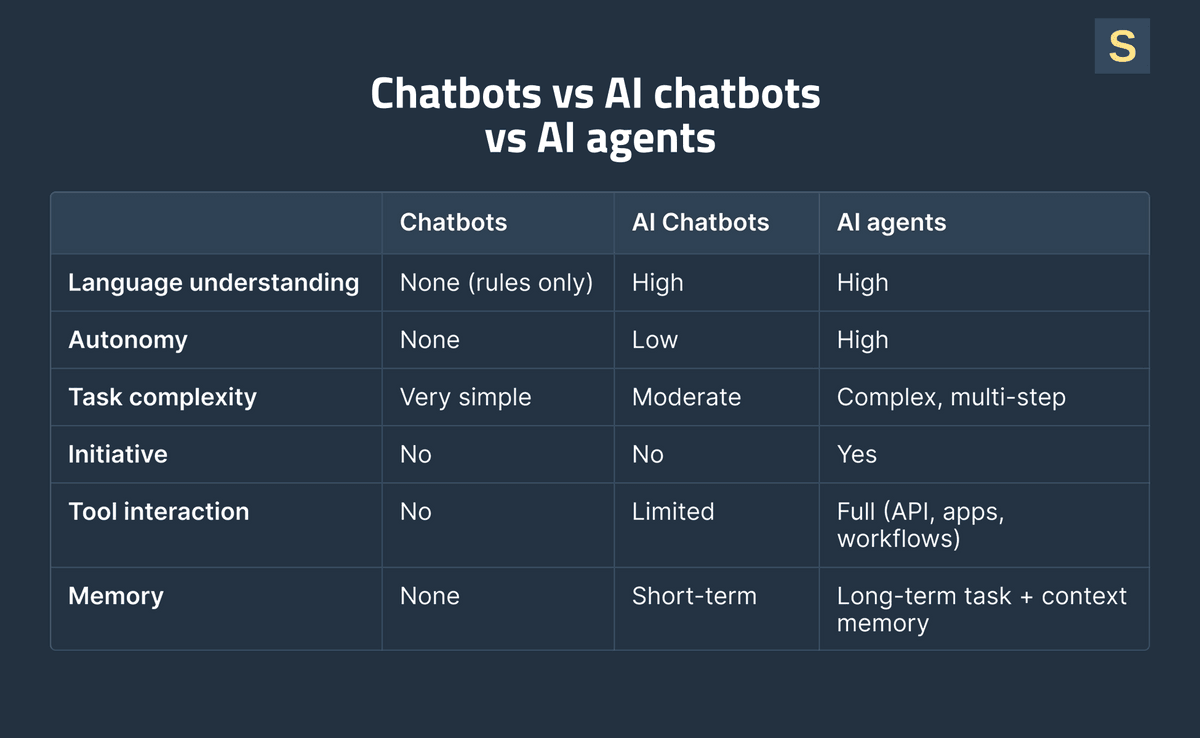
What Is the Difference Between Chatbots and AI Agents?
Both AI chatbots and AI agents are designed to reduce human effort by automating repetitive tasks. The key difference lies in technical depth.
- AI chatbots usually follow scripts or basic machine learning. They handle simple, one-step tasks such as answering common questions.
- AI agents use advanced AI models, remember context, make decisions, and work with external tools or APIs. They can plan and complete multi-step tasks on their own, not just reply to messages.
Both solutions are suitable for similar use cases, but produce slightly different outcomes. For example, in customer support, an AI chatbot can answer FAQs about order status, return policies, or business hours. In this case, they follow predefined scripts or keyword-based rules.
In contrast, an AI agent can handle more complex scenarios, such as investigating a delayed order by accessing multiple backend systems (inventory, shipping, and CRM). They can also apply company policies to issue refunds or discounts, update the customer automatically, and even schedule follow-up actions if additional steps are required.
How to Choose Between an AI Agent vs Chatbot
Now that you understand the difference between AI agents and AI chatbots, the next step is to choose the best solution for your business. While AI agents are more advanced, their implementation isn’t always justified, as they are more complex and expensive to build.
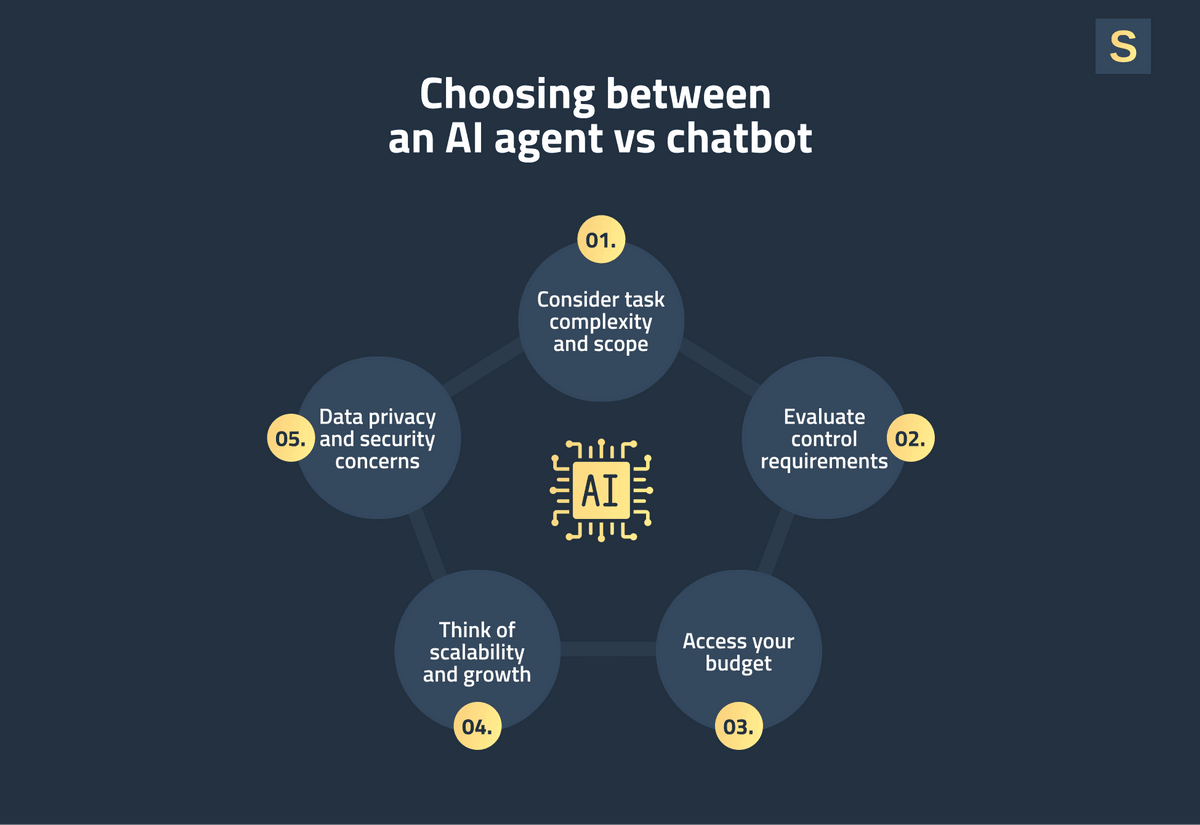
To make the right decision, start by asking yourself these five questions.
1. How Complex is Your Business Task?
There’s no need to implement complex AI agents for simple, single-step tasks. If your goal is to automate bookings, answer website FAQs, or help users navigate your knowledge base, a well-designed AI chatbot will be more than enough.
2. What Level of Control Do You Need
Since AI agents operate autonomously and rely on large, flexible datasets, it becomes much harder to control or predict their responses. They can generate unexpected outputs or take unplanned actions.
For some businesses, especially those in regulated industries or those with strict brand-voice requirements, this lack of control can be a significant risk. In such cases, a traditional AI chatbot may be the safer and more practical choice.
3. What Is Your Budget?
One of the biggest mistakes founders make when planning budgets for AI projects is focusing solely on development and overlooking ongoing maintenance. AI models require regular retraining, updates, and a flexible infrastructure that can scale as your user base grows.
When choosing between AI agents and AI chatbots, it’s important to understand that AI agents demand significantly more investment in development and support. They often rely on multiple data sources, require continuous optimization, and need more complex monitoring to ensure they behave reliably over time.
Read also: How to Estimate SaaS Development Costs
4. Are There Specific Data Privacy and Security Requirements?
AI chatbots are generally easier to secure because they handle limited, low-risk data. This makes them a good solution for companies with basic security requirements.
AI agents, on the other hand, often access information across multiple systems. This can include sensitive data such as billing details, personal health information, or internal documents. As a result, you will need to implement stricter controls and ongoing risk management to ensure compliance with regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR.
5. What Are Your Growth Plans?
You should also think about scalability in advance. As your user base grows, your system must grow accordingly.
AI chatbots are easier to scale horizontally. They handle limited, predictable tasks, so adding more users typically just requires more server capacity or cloud instances.
AI agents are harder to scale. It often involves managing model retraining, memory storage, and real-time access to external systems. This can be costly and technically challenging. Also, high user volume can impact response speed or system reliability if the architecture isn’t carefully designed.
So, the verdict:
You should choose AI chatbots when:
- You need a solution for simple, one-purpose tasks such as FAQs, basic support, and info retrieval.
- Your use case is narrow, with predictable inputs and outputs.
- You want strong control over exact responses and brand voice.
You should choose AI agents when:
- You have complex, multi-step processes spanning multiple systems.
- You need context-awareness, personalization, and adaptability.
- You’re ready to invest in infrastructure, integration, and governance to get deeper automation benefits.
Read also: How to Implement AI into Your SaaS Application
Agentic AI platforms vs Traditional Chatbot Builders Comparison
Now, let’s dive a bit deeper into implementation. AI agents and AI chatbots have different requirements when it comes to architecture, infrastructure, and security. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right approach for your project.
Traditional Chatbot Builders are tools or frameworks used to build mostly rule‑based or keyword‑based bots. They rely on static decision trees, prebuilt response templates, and minimal logic.
Agentic AI Platforms are systems built around large language models (LLMs) plus integrations, reasoning and planning, memory and context, and tool‑API orchestration.
What this means for implementation and architecture:
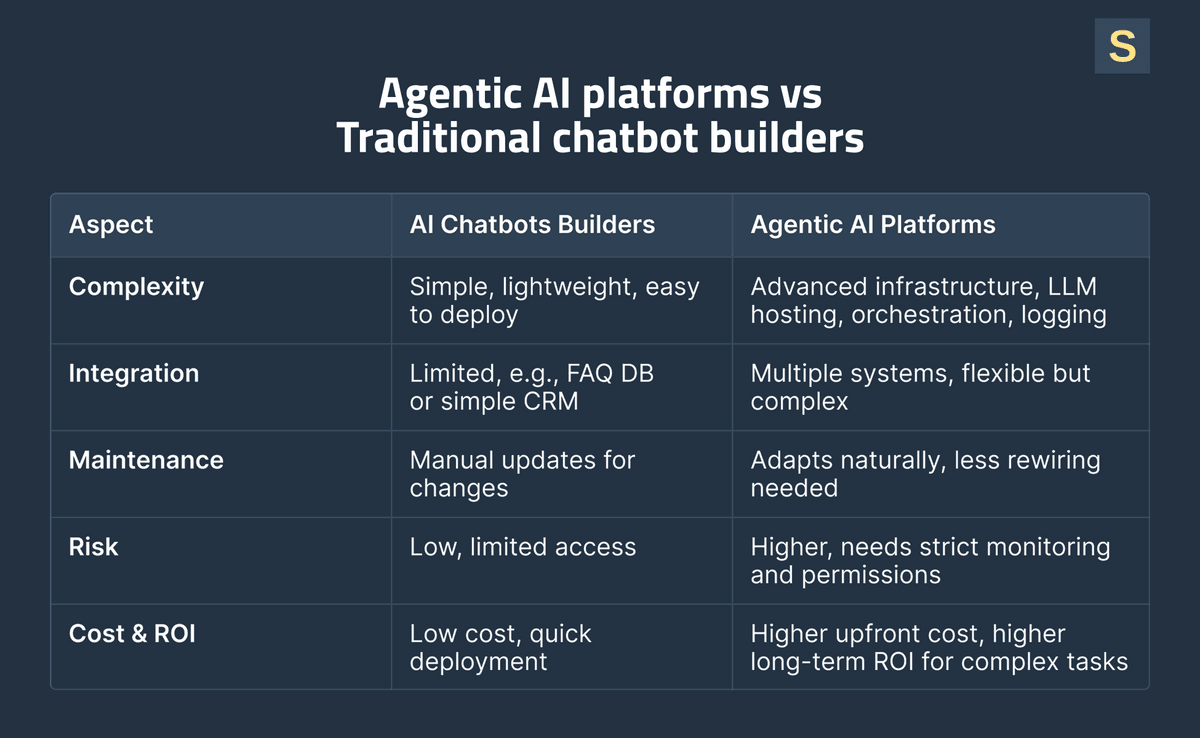
- Complexity & Infrastructure: Agentic AI requires a more advanced infrastructure, including LLM hosting/inference, orchestration layer, API gateways, memory/state storage (databases or NoSQL), logging/audit systems, and error handling. Chatbots are typically far lighter and easier to deploy.
- Integration Scope: With agents, you often need to integrate many backend systems. This adds complexity but also flexibility. Chatbots may only need a static FAQ database or simple CRM lookup.
- Maintenance & Flexibility: Traditional bots need manual updates when business logic changes. Agents, by contrast, may handle a wider variety of inputs without explicit rewiring.
- Risk & Governance: Because agents act autonomously and can modify backend systems, it’s crucial to set up robust logging, permission controls, and monitoring. AI chatbots are lower-risk by design.
- Cost & ROI: Agentic AI requires a higher upfront investment (development, infrastructure, integration), but can deliver greater automation depth and ROI over time for complex tasks. Chatbots are quicker and cheaper to deploy.
Also, you’ll need experienced engineers who combine classical engineering and AI expertise for both types of solutions. Working with a proven engineering team will help you avoid costly rework and achieve greater efficiency.
Implement Efficient AI Solutions with Seedium
At Seedium, we cultivate in-house AI expertise to help our clients build smarter software products. Our approach is to go beyond implementing AI for the sake of it, making sure the chosen solution can really help businesses reach their goals.
With over 200 delivered projects and 8+ years of experience in the market, Seedium is trusted worldwide. 90% of our clients maintain long-term relationships with the company, considering us a reliable software development provider.
Feel free to check out our AI development and integration services or contact us using the form below to discuss your project.