For healthcare providers and digital product companies, staying on top of tech trends is no longer a business choice or a strategic consideration, it's a necessity. Regardless of your company's size, understanding which innovations matter can help you stay competitive, scale efficiently, and deliver more value to your users.
At Seedium, we work closely with healthcare startups and established medical providers to help them build, grow, and modernize their digital products. Our broad and diversified experience allows us to anticipate and stay ahead of emerging trends.
In this article, we’ll recap the top 10 healthcare technology trends for 2026 and offer practical tips on how to apply them to your business, whether you're creating a new solution or working on an existing one.
Overview of Key Healthcare Technology Trends in 2026
The healthcare technology market is booming and shows no signs of slowing down. Statistics project that in 2025, the digital health market will be worth over $660 billion, driven by increased demand for virtual support services, as well as AI-powered and data-driven solutions that optimize outcomes for patients and providers. Similarly, MarketsandMarkets forecasts a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.8% from 2024 to 2029, highlighting how quickly the landscape is evolving.
AI in healthcare market size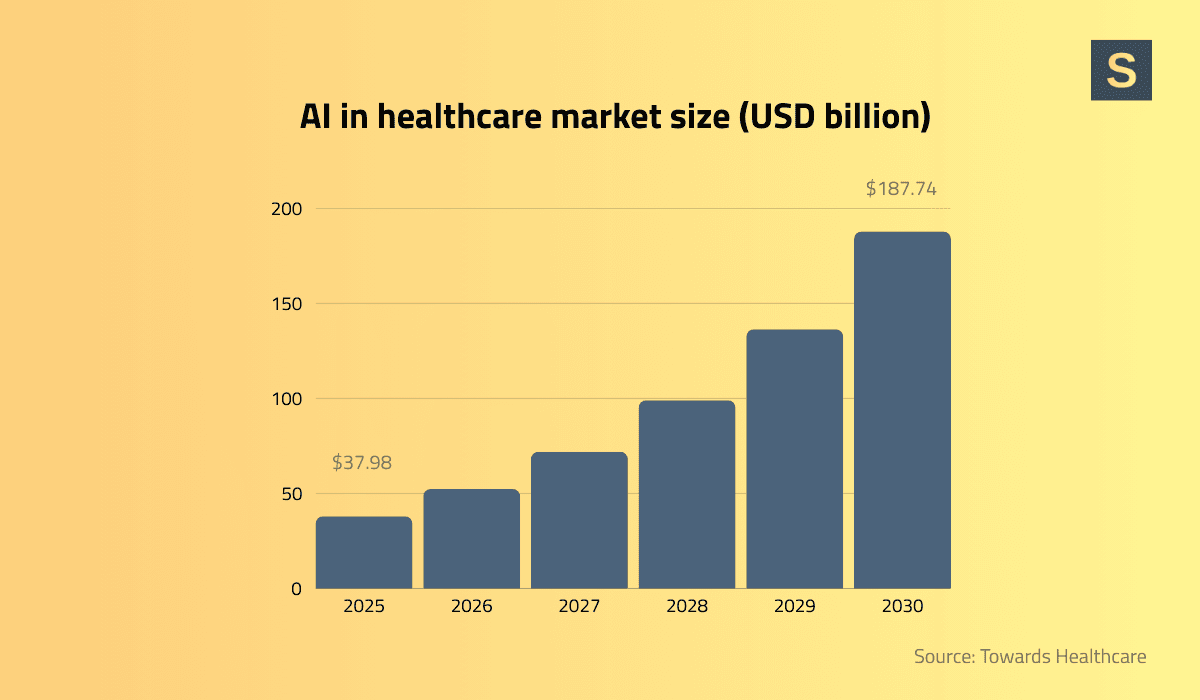
In this rapidly changing world, startups and SMEs are best positioned to innovate and often have an edge when it comes to adopting new technology faster. However, success is achieved not just through early access, but also through strategy. To compete and stay current, companies must focus on technological trends in healthcare that address user needs, comply with health regulations, and offer scalability.
Trend #1: Turning Data into Insights with AI
AI is often associated with advanced medical applications that detect diseases. However, many ethical, safety, and compliance challenges limit the implementation of AI-based diagnostic systems outside of research institutions or large healthcare systems. For SMEs and startups, managing and analyzing data are among the most realistic and scalable uses of AI.
AI can significantly improve the structure of medical data used in healthcare operations and delivery. For example:
- Automating medical data input through natural language processing (NLP), converting unstructured notes, lab tests, or discharge reports into structured, searchable data.
- AI analytics platforms that facilitate early intervention by identifying at-risk patients or predicting treatment outcomes based on historical data.
- Streamlining claims and billing with intelligent cross-checking of treatment codes and insurance data, reducing administrative burden and revenue loss.
- Increasing operational efficiency, such as resource planning, staffing, and inventory management based on data insights.
AllClinics: A real-world example of an AI-powered platform in healthcare
At Seedium, we harnessed the power of AI data analytics in our product, AllClinics. This platform uses AI to collect and process data about every hospital in the United States, from service lists to cost breakdowns by location.
This offers benefits to both patients and providers:
- For patients: Transparent information about the cost and quality of care.
- For payers and providers: Reliable comparative data without the need to build internal analytics platforms.
AI isn’t just about futuristic diagnoses. When used to process and analyze healthcare data, it becomes a valuable tool for reducing costs, streamlining processes, and empowering care teams and patients. For digital health startups and companies, it’s a strategic differentiator that can scale with business growth.
Read more about this case study here.
Trend #2: Automating Administrative Tasks
 AI in healthcare market overview
AI in healthcare market overview
AI can do a tremendous job in automating administrative processes and managing data. This relieves the burden on staff and reduces the risk of human error. AI significantly simplifies and systematizes the very “invisible” work, which accounts for up to 30% of all healthcare expenses. This is a massive layer of manual operations, from scheduling appointments to invoicing, where an error costs time, money, and even reputational risks.
According to MDINetworx, integrating AI into healthcare data processes improves the quality of patient care and management decisions. Automating routine administrative tasks can reduce time spent by up to 40%, freeing up resources for growth and improving the quality of care.
Trend #3: Adopting AI Agents for Healthcare
AI agents represent the next generation of AI in healthcare: more capable, autonomous tools that not only respond to directives but also act independently, scan context, and interact with clinical information in real time. It’s essential to understand their conceptual difference from traditional chatbots, namely, the ability to think in context:
- Monitoring and reporting on a patient’s condition, sending personalized notifications (medication reminders, visit directions, medication information);
- Automatically filling forms to reduce workload and improve data quality;
- Supporting the clinical decision-making process (including prompts based on medical history and current symptoms);
- Enabling seamless interactions with patient portals and telemedicine platforms.
According to forecasts, AI agents will become integral to digital healthcare, particularly in outpatient and remote models. Their use will become ubiquitous, from call centers to electronic health records (EHR), where they automatically summarize visits and predict potential risks. The integration of such solutions can save up to 20–30% of staff time and increase patient satisfaction, especially in the context of an overburdened traditional healthcare system.
In our approach to developing digital products for health tech, we already consider AI agents a promising component of the next generation of solutions. Therefore, when designing the interface, we recommend establishing an architecture that allows for the future integration of agents capable of processing both text and voice information. This enables process automation that is truly "smart" and adaptive to each user.
Deploying AI agents as one of the healthcare technology trends doesn’t require building a large-scale ML infrastructure from scratch. Currently, APIs (e.g., from OpenAI, Google Vertex AI, or IBM Watson Health) allow for easy integration of agents with minimal capital investment, while still maintaining scalability.
Trend #4: Experimenting with IoMT for Patient Monitoring
Although "digital medicine" has, for many, come to mean apps and platforms for scheduling appointments or virtual consultations, the fundamental transformation is occurring through IoMT, the Internet of Medical Things. This ecosystem of interconnected medical devices, software, sensors, and cloud platforms enables the continuous collection, analysis, and transmission of patient physiological data.
Key benefits of IoMT include:
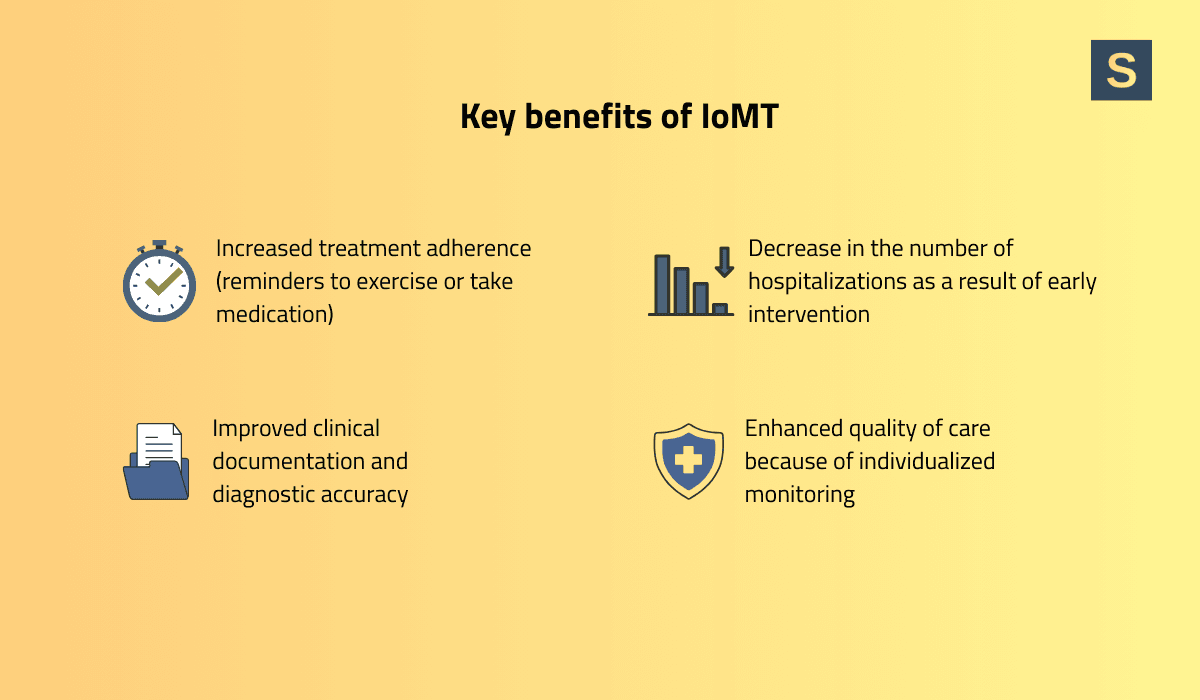
- Enhanced quality of care through individualized monitoring;
- Fewer hospitalizations due to earlier interventions;
- Improved clinical documentation and diagnostic accuracy from objective data;
- Increased treatment adherence via reminders for medication, physical therapy, or exercise.
IoMT devices provide continuous, real-time health monitoring, from pulse rate to glucose levels, to detect abnormalities and intervene before complications arise. These devices ease the burden on clinics, particularly when caring for chronically ill patients or those in post-operative recovery. When integrated with AI, data from wearable devices becomes the foundation for predictive analytics, improving treatment efficiency and reducing hospital costs.
The global IoMT market is projected to reach $244.4 billion by 2029, up from $97.7 billion in 2025. This confirms the sector's long-term investment appeal and the growing interest in remote care technologies.
Trend #5: Improving Telemedicine and Remote Patient Care
Telemedicine confidently remains in the top 10 technology trends in healthcare. It has evolved beyond simple video consultations into a smoother and more advanced system. Healthcare startups are driving innovation through:
- Remote integrated diagnostics: Health professionals can now diagnose patients remotely using equipment that records biometrics such as heart rate, oxygen saturation, and blood pressure. These readings are securely transmitted for analysis, enabling more accurate and comprehensive remote care.
- Intelligent scheduling and triage automation: AI-powered systems improve scheduling efficiency, reduce wait times, and automate triage processes to prioritize urgent cases. This allows medical facilities to operate more effectively and provide timely care to critical patients.
- Improved access for underprivileged populations: Telemedicine is bridging healthcare gaps for time-constrained or geographically underserved communities. It helps overcome barriers like physical distance, transportation issues, and provider shortages, expanding access to specialty care.
Challenges remain, including user adoption, reimbursement policies, and platform reliability. However, the most significant innovations are addressing these pain points to ensure telemedicine platforms are as seamless, accessible, and user-friendly as possible, for both patients and providers.
Trend #6: Enhancing Infrastructure Scalability with the Cloud
Technology trends in healthcare can't be considered without the cloud. Cloud technologies have become essential as healthcare organizations scale operations. In the coming years, startups and SMBs will focus on the following advancements:
- Shifting from hybrid to cloud-native solutions: More businesses are transitioning from hybrid systems (combining on-premises and cloud apps) to fully cloud-native solutions. This move provides greater flexibility, cost savings, and the ability to quickly scale with demand
- Low-latency edge computing applications: Edge computing is increasingly applied to real-time, low-latency use cases such as remote surgeries and 24/7 patient monitoring. By processing data closer to its source, edge computing reduces latency and boosts the effectiveness of mission-critical applications.
- Classic AI predictive analytics services: The cloud’s computing power supports AI-driven predictive analytics. Clinical teams use this to screen patients, forecast treatment outcomes, and improve decision-making, thereby enhancing the overall patient experience.
However, adopting cloud technology also presents challenges, primarily around regulatory compliance (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR, CCPA). Organizations must implement strong, privacy-based compliance programs to protect user data.
Choosing a cloud provider is a long-term decision, and switching providers can be costly and complex. Healthcare organizations must be mindful of the risk of vendor lock-in, particularly when deploying large-scale applications.
Trend #7: Addressing Challenges of EHR Interoperability
Despite decades of effort, electronic health record (EHR) interoperability remains one of the most pressing issues in healthcare. However, this year promises significant improvements:
- APIs minimize variability among EHR systems, enabling secure, real-time data exchange between medical service providers and institutions. APIs are built with robust security controls, providing stable and transparent system connectivity.
- Interoperability testing of blockchain: Blockchain is being explored as a way to securely share health data without relying on central authorities. As a decentralized and tamper-evident ledger, blockchain may enable secure, transparent data sharing between systems.
- FHIR-based platforms gain traction: Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR), a rapidly growing standard, is increasingly adopted for its ability to support fast, secure, and interoperable data exchange. Some health startups have launched FHIR-based platforms to streamline data sharing between healthcare systems.
While these healthcare technologies are promising, demand for comprehensive EHR interoperability solutions persists, especially for multi-vendor network startups, where integration is more challenging due to the variety of systems involved. As data exchange efficiency becomes more critical, innovations in APIs, blockchain, and FHIR will be key to solving the interoperability challenge.
Trend #8: Strengthening Cybersecurity and Compliance
As healthcare continues to digitize at an accelerated pace, cybersecurity threats have increased in parallel. No matter how technology trends in healthcare change, security remains at the top.
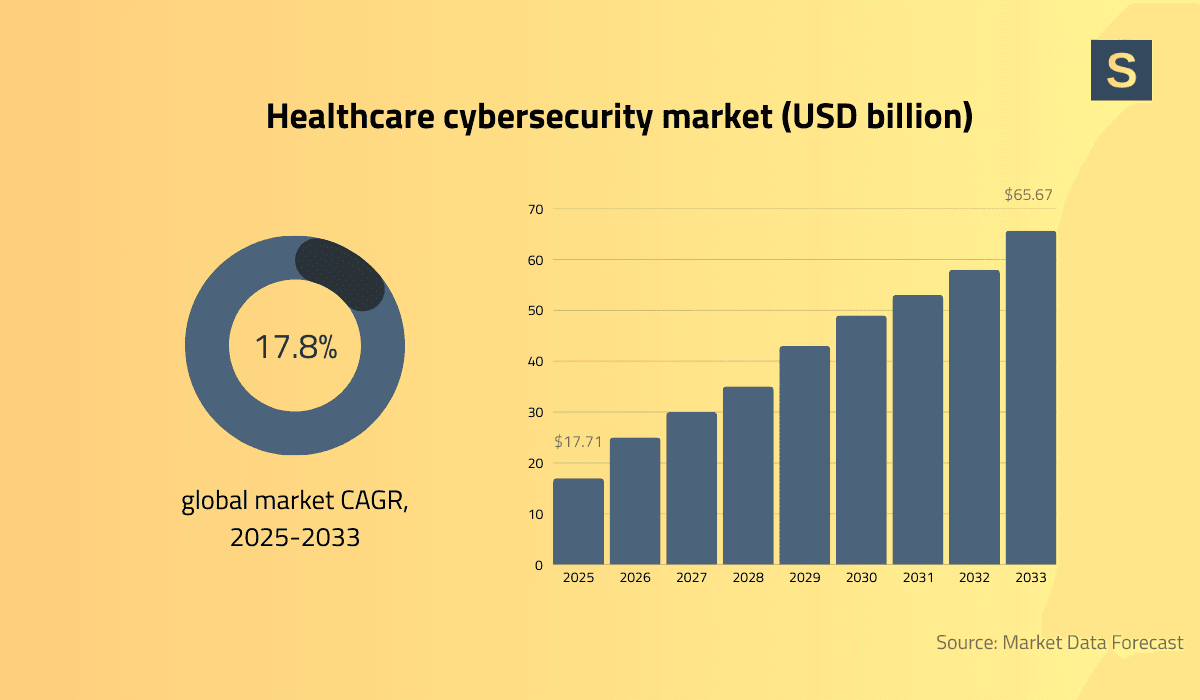
To address this, healthcare providers are investing significant capital into the following critical areas:
- Zero Trust Architectures: These security models operate on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” regardless of whether users or devices are inside or outside the network. This approach is becoming a new standard in healthcare cybersecurity. Strong verification is required for all users and devices, enhancing overall system security.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Given the sensitivity of patient data, IAM technologies are essential for authenticating access based on credentials and roles. IAM helps ensure only authorized individuals can access medical information, which is vital for meeting stringent healthcare regulations.
- Real-time threat detection and AI-powered security software: AI and machine learning are increasingly used to detect cyber threats as they happen. These tools identify unusual data patterns or user behavior, enabling quicker responses to potential breaches before significant damage occurs.
Healthcare professionals must walk a fine line between embracing innovation and maintaining data security. Protecting sensitive patient information, ensuring compliance with regulations such as HIPAA, and addressing growing patient and regulatory expectations remain top priorities.
Read also: How to Make Your App HIPAA-compliant: Best Practices & Checklist
Trend #9: Immersive Simulations for Medical Training in VR
Virtual reality, or VR, once a novelty video game, has now become a fundamental medical training and education tool. As one of the technology trends in healthcare, VR technology is used in the following key ways:
- Surgical and emergency simulations: VR allows medical students and medical professionals to practice complex surgical procedures or perform emergencies without risking patients' lives. Virtual simulations allow for repetitive practice, which helps build muscle memory and sharpen skills.
- The patient empathy value of the simulations: VR also enables clinicians to experience firsthand what it’s like to be a patient. With vision and seeing from that of a patient, doctors, nurses, and other medical caregivers might become more empathetic, improve their bedside manners, and be attuned to what it is to cope with patients' emotional and physical demands.
- Train nurses and physicians without real risks: Physicians and nurses can use VR to rehearse procedures in a risk-free, simulated environment and apply them to real patients. It increases their skills and confidence and reduces medical complications.
With the demand for immersive learning growing in medical schools and hospitals, startups have a huge opportunity to create VR-based solutions that meet the changing demands of medical education.
Trend #10: The Rise of Fitness & Wellness Apps
As health and wellness continue to be top consumer priorities, the market for digital wellness solutions is booming. It is projected to exceed $200 billion by the end of 2025. Healthcare providers and startups are focusing on:
- AI-driven personalized exercise routines: AI uses individuals’ health data, goals, and history to create and adjust exercise plans dynamically. These routines evolve to keep users engaged and help them achieve their fitness objectives.
- Mindfulness and therapy apps: Mental health is more important than ever. Both startups and established healthcare organizations are developing apps that address stress, anxiety, and other mental health concerns through guided therapy, mindfulness exercises, and meditation.
- Corporate wellness solutions: As companies prioritize employee well-being, the demand for corporate wellness programs continues to rise. Businesses are investing in solutions that promote physical fitness and mental health, leading to healthier, more productive teams.
With the growing emphasis on preventative healthcare, companies entering the wellness space must demonstrate measurable results and ensure full compliance with regulatory standards and health guidelines.
Best Practices for Applying Healthcare Technology Trends in 2025
Success lies not in adopting every trend, but in choosing the right ones for your specific goals. Understanding a healthcare technology trend is only the starting point. Real value comes from aligning innovation with actual business needs. With numerous options available, it’s essential to ask: What are the most significant trends in healthcare technology for your audience and operational objectives?
Here are the best practices to achieve that:
- Establish clear business objectives: Ensure the trend you adopt addresses real issues for your patients and enhances outcomes. Not all innovations suit every model.
- Consult with experts: Seedium can help determine the feasibility of incorporating new technology and create a step-by-step process tailored to your product.
- Begin small: Roll out one significant feature to test its utility and gather feedback before a broader release.
- Observe and adapt: Closely monitor KPIs and be willing to pivot if the chosen trend does not perform as expected.
- Evaluate long-term impact: Invest in technologies that demonstrate lasting growth, user adoption, and long-term value.
With strategy-informed decision-making, healthcare startups can cut through the noise and focus on breakthroughs that create meaningful impact.
Top 3 Future Trends in Healthcare Technology
Looking ahead to 2026 and beyond, healthcare will continue to evolve with the aid of technology, presenting both challenges and opportunities for startups and long-established providers. Below are three of the most critical medtech trends to follow:
- AI and predictive analytics are a must for future success. Artificial intelligence is not a substitute in healthcare, especially in predictive analytics and individualized care, but a transformational force. Among new trends in healthcare technology, AI stands out. Startups that leverage AI tools for process optimization, improved decision-making, and personalized care will be positioned for success. The ability to depersonalize cost recovery while maximizing patient outcomes will define the most innovative players in the industry.
- Genomics is the driving force behind the shift to personalized medicine. One of the most impactful trends in healthcare technology, genomics is reshaping how we approach treatment precision and disease prevention. Genomic technology enables clinicians to tailor treatments to a person’s unique genetic makeup, exponentially increasing efficacy. Its continued adoption will lead to more targeted care and earlier detection and prevention of disease.
- Robotics and automation are improving patient care. Robotics is transforming healthcare, from minimally invasive surgeries to robot-assisted therapy. As demand for effectiveness and precision rises, providers that develop and implement robotics solutions will be best positioned to improve patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
Wrapping up
Healthcare technology is on the cusp of a major transformation. By staying grounded in current trends while embracing emerging innovations, healthcare startups and established providers can reshape the industry landscape.
Need help navigating these trends? Check out our healthcare software development services and contact us to start a project.