Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment, or CI/CD, is a DevOps practice that accelerates software development cycles by automating the building, testing, and deployment processes.
What is the Difference between Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment?
Continuous integration ensures that code changes are made to the main branch early and often, with automated testing of these changes. Each integration triggers automated builds and tests, ensuring that new code works correctly with the existing codebase. This allows you to identify errors and security issues early, before they compound.
Continuous deployment, or continuous delivery, is the next step after CI that takes automation further. It automates the deployment of code that has passed CI’s build, unit, and integration tests to a release-ready repository.
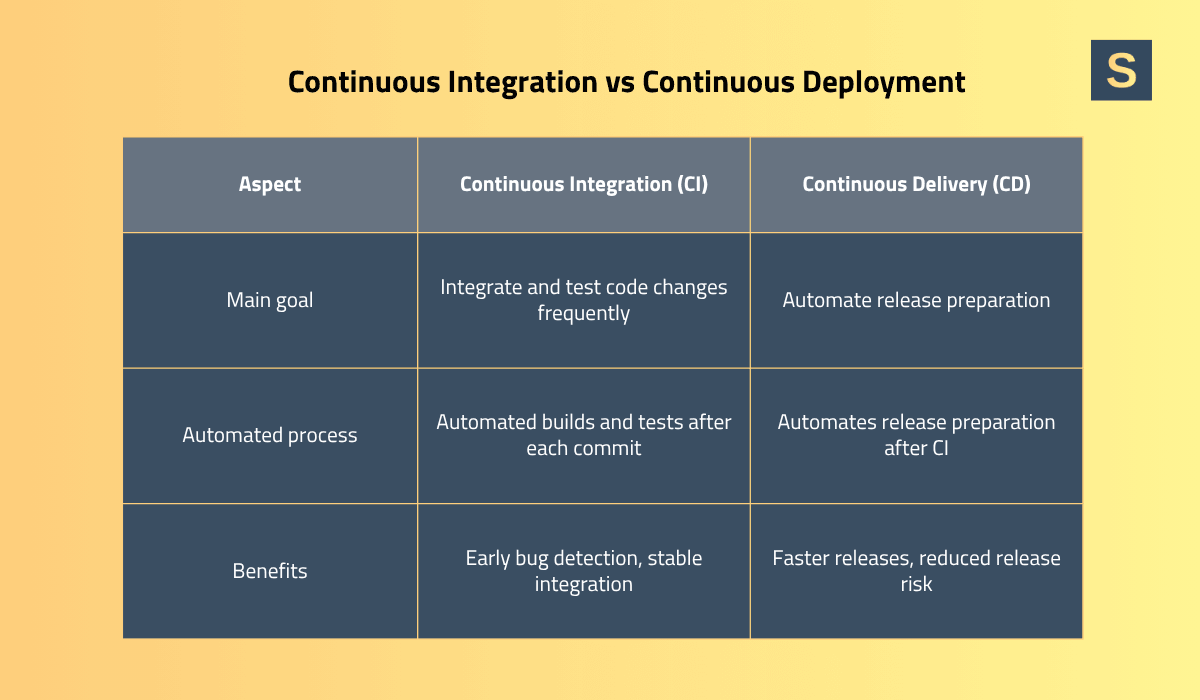
So, Continuous Integration (CI) focuses on merging and testing code frequently, while Continuous Delivery (CD) focuses on automating the release process up to the point of deployment.
What is a CI/CD Pipeline?
A CI/CD pipeline is a set of automated processes that software developers use to streamline the building, testing, and deployment of software solutions.
Setting up CI/CD pipelines increases the efficiency and reliability in the development process. It’s considered the best practice for building SaaS applications and other types of modern software.
What are the Benefits of CI/CD?
CI/CD not only speeds up software delivery but also helps engineers improve quality, reliability, and team efficiency. Here are the key advantages of implementing it into the development workflow.
- Faster development and delivery by automating repetitive tasks and enabling frequent releases and updates.
- Early detection of errors, bugs, and code conflicts, reducing the cost and complexity of fixing later.
- Improved code quality by ensuring that only validated, stable code progresses.
- Increased reliability thanks to predictable and repeatable releases.
- Faster feedback loops by testing features earlier in the development cycle.
- Improved collaboration and scalability.
How to Implement CI/CD
The process of establishing CI/CD pipelines for software development consists of the following steps:
- Setting up version control: Use Git (GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket) and organize branches to track changes and prevent code conflicts.
- Choosing the right tech stack: Pick a CI/CD platform like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI/CD, or CircleCI.
- Automating the build: Define build scripts to ensure code compiles correctly.
- Implementing automated testing: Run unit, integration, and code quality tests to detect bugs before they reach production.
- Setting up Continuous Integration: Merge code frequently into a main branch, with CI validating every merge.
- Setting up Continuous Delivery/Deployment: Auto-deploy to staging, reducing downtime and risk in production releases.
- Configuring monitoring and alerts: Ensure system monitoring to catch production issues early.
- Optimizing: Keep the pipeline efficient, adapting to team growth and project complexity.
Start with automating the most critical steps, and then iterate by gradually adding additional optimizations to make the CI/CD pipeline more robust and efficient.
Check out more SaaS terms in our SaaS glossary for business leaders.
Build and Scale Your Software Products with Seedium
Seedium is a trusted web & mobile development company that helps businesses build and scale their software solutions. Since 2017, we have successfully launched over 200 products in more than 15 industries, including SaaS, HRTech, and HealthTech.
Seedium offers a wide range of design & development services to help you achieve your business goals efficiently:
- Web & mobile application development;
- UX/UI & product design;
- Custom software development & integrations;
- AI development;
- Scaling product architecture;
- Providing dedicated development teams.
Feel free to contact us to start a conversation about your project. Let’s build something great together!




